📉 The Role of Cognitive Biases in Portfolio Underperformance
Investing is often portrayed as a rational endeavor driven by data and analysis. However, beneath the surface, human psychology plays a significant role in shaping investment decisions. Cognitive biases systematic patterns of deviation from norm or rationality in judgment—can lead investors to make choices that deviate from optimal strategies, often resulting in portfolio underperformance. This article delves into how these biases manifest in investment behavior and offers strategies to mitigate their impact.
🧠 Understanding Cognitive Biases in Investing
Cognitive biases are inherent in human decision-making processes. In the context of investing, these biases can cloud judgment, leading to suboptimal investment choices. Some common cognitive biases affecting investors include:
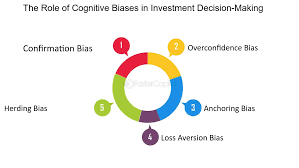
- Overconfidence Bias: Investors may overestimate their knowledge or ability to predict market movements, leading to excessive trading or risk-taking.Latest news & breaking headlines+5Wikipedia+5holmes-griffeth.com+5
- Anchoring Bias: Relying too heavily on the first piece of information encountered (the “anchor”) can skew subsequent judgments, such as holding onto a stock purchased at a high price despite its declining value.holmes-griffeth.com
- Recency Bias: Placing undue weight on recent events or trends can cause investors to chase past performance, potentially buying into overvalued assets.
- Loss Aversion: The tendency to prefer avoiding losses rather than acquiring equivalent gains can lead to holding onto losing investments for too long, hoping to break even.Toptal+5Latest news & breaking headlines+5Wikipedia+5
- Confirmation Bias: Seeking out information that confirms pre-existing beliefs can result in ignoring critical data that contradicts one’s investment thesis.Investopedia
📊 Impact on Portfolio Performance
The influence of cognitive biases on investment decisions can lead to several detrimental outcomes:
- Excessive Trading: Overconfidence can lead to frequent trading, increasing transaction costs and potentially reducing returns.
- Poor Diversification: Biases like home bias can result in a lack of diversification, exposing portfolios to unnecessary risks.Financial Times+1Latest news & breaking headlines+1
- Chasing Performance: Recency bias may drive investors to invest in assets that have recently performed well, often at inflated prices, leading to poor future returns.Barron’s+3holmes-griffeth.com+3Latest news & breaking headlines+3
- Emotional Decision-Making: Loss aversion can cause investors to make emotionally driven decisions, such as selling winners too early or holding onto losers too long.
🛡️ Strategies to Mitigate Cognitive Biases
While it’s challenging to eliminate cognitive biases entirely, investors can adopt strategies to minimize their impact:
- Develop a Clear Investment Plan: Establishing a well-defined investment strategy with set goals and criteria can help counteract impulsive decisions driven by biases.
- Regular Portfolio Reviews: Periodic assessments of portfolio performance can identify and correct biases that may have influenced investment choices.Wikipedia
- Seek Objective Advice: Consulting with financial advisors or using automated investment tools can provide an external perspective, helping to counteract personal biases.
- Educate Yourself: Understanding common cognitive biases and their effects on decision-making can increase self-awareness and improve investment outcomes.
✅ Conclusion
Cognitive biases are an inherent part of human decision-making and can significantly impact investment outcomes. By recognizing and understanding these biases, investors can take proactive steps to mitigate their effects, leading to more rational and potentially more successful investment strategies.
Read more: https://wealthfitlife.com/the-rise-of-tactical-asset-allocation-beyond-60-40-portfolios/
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What are cognitive biases in investing?
- Cognitive biases are systematic patterns of deviation from norm or rationality in judgment, which can lead investors to make irrational investment decisions.
- How does overconfidence bias affect investment decisions?
- Overconfidence bias can lead investors to overestimate their knowledge or ability to predict market movements, often resulting in excessive trading or risk-taking.
- What is anchoring bias in the context of investing?
- Anchoring bias occurs when investors rely too heavily on the first piece of information encountered, such as an initial stock price, which can skew subsequent investment decisions.Wikipedia
- How does recency bias influence investment behavior?
- Recency bias causes investors to place undue weight on recent events or trends, potentially leading them to chase past performance and invest in overvalued assets.holmes-griffeth.com
- What is loss aversion and how does it impact investing?
- Loss aversion is the tendency to prefer avoiding losses rather than acquiring equivalent gains, which can lead investors to hold onto losing investments for too long.
- How can confirmation bias affect investment decisions?
- Confirmation bias leads investors to seek out information that confirms pre-existing beliefs, potentially ignoring critical data that contradicts their investment thesis.
- What are the consequences of cognitive biases on portfolio performance?
- Cognitive biases can lead to excessive trading, poor diversification, chasing performance, and emotional decision-making, all of which can negatively impact portfolio performance.
- Can cognitive biases be eliminated in investing?
- While it’s challenging to eliminate cognitive biases entirely, investors can adopt strategies to minimize their impact, such as developing a clear investment plan and seeking objective advice.
- How can regular portfolio reviews help mitigate cognitive biases?
- Periodic assessments of portfolio performance can identify and correct biases that may have influenced investment choices, leading to more rational decision-making.
- Why is investor education important in mitigating cognitive biases?
- Understanding common cognitive biases and their effects on decision-making can increase self-awareness and improve investment outcomes.
📚 Academic References
- Barber, B. M., & Odean, T. (2000).
Trading is hazardous to your wealth: The common stock investment performance of individual investors.
Journal of Finance, 55(2), 773–806.
https://doi.org/10.1111/0022-1082.00226
➤ Discusses how overconfidence leads to excessive trading and underperformance. - Kahneman, D., & Tversky, A. (1979).
Prospect theory: An analysis of decision under risk.
Econometrica, 47(2), 263–291.
https://doi.org/10.2307/1914185
➤ Introduces loss aversion and the psychological biases affecting decisions under risk. - Tversky, A., & Kahneman, D. (1974).
Judgment under Uncertainty: Heuristics and Biases.
Science, 185(4157), 1124–1131.
https://doi.org/10.1126/science.185.4157.1124
➤ Foundational study on cognitive heuristics such as anchoring and availability bias. - Statman, M. (2010).
What Investors Really Want: Know What Drives Investor Behavior and Make Smarter Financial Decisions.
McGraw-Hill.
➤ Discusses investor behavior, biases, and the gap between rational and actual behavior. - Baker, H. K., & Nofsinger, J. R. (2010).
Behavioral Finance: Investors, Corporations, and Markets.
Wiley.
➤ Comprehensive overview of behavioral finance including cognitive and emotional biases.
